Curriculum
Derivatives
Introduction to Derivatives
0/11-
Introduction Video - Derivatives
-
What is a Derivative?
-
Definition of Derivatives
-
Types of Derivatives
-
Features of the Derivative Contract
-
Trading and Settlement of Derivatives
-
Participants in Derivative Markets
-
Size of the Derivative Market
-
Significance of Derivative Market
-
Criticism of Derivative Market
-
Quiz - Introduction to Derivatives
Forward Contract
0/7OTC vs Exchange Traded Instruments
0/8Futures Contract
0/17Options
0/11Swaps
0/37Criticism of Derivative Market
Derivative products were mainly responsible for some historical collapses or bankruptcies of some of the following major financial institutions – Barings Bank (1995), Long-term Capital Management (1998), Enron (2001), Lehman Brothers, and American International Group (AIG) in 2008. Derivative products are widely criticised because of the 2007-08 credit crisis that plunged the global economy into recession. Some products such as the Credit Default Swaps are also termed as ‘financial weapons of mass destruction’. Other derivative products that were created using mortgages as the underlying, also became worthless when the housing prices declined and the counter parties defaulted on promised payments. However, it is the insatiable greed and the irresponsible use of these contracts (and not the contract itself) that must be blamed for the economic catastrophe.



Other notable points are –

High risk – The use of Leverage enhances return, but it also enhances the risk that the losses could be equally substantial, especially if the markets become volatile. The risk of counterparty defaulting on fulfilling its promised obligations is also common in OTC derivative contracts.
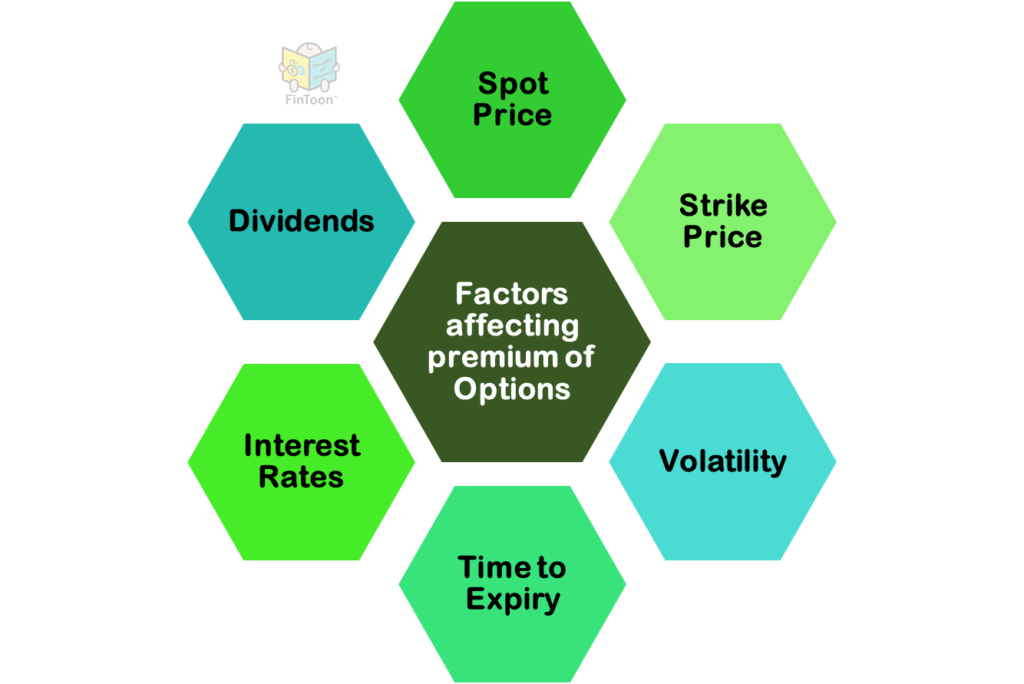
Complexity – Most contracts are very sensitive even to small changes in factors such as spot rates, interest rates, currency rates, volatility, time to maturity, etc. Though complex mathematics may be theoretically correct, the financial models on which derivative pricing is based can break down due to irrational behaviour portrayed by FMPs (Financial Market Participants). It is very difficult to incorporate psychological factors as quantifiable variables in such models when trying to find the intrinsic value of such instruments.
 Excessive Speculation – hedgers require speculators to take the opposite side of the trade. A high number of speculators makes it cheaper and easier to hedge. But speculators are opportunists who try to corner the market and seek to make short-term profits by engaging in price and volume manipulations. One way of curtailing these short-term manipulative trading activities is by imposing higher taxes on short-term profits as compared to long-term capital gains.
Excessive Speculation – hedgers require speculators to take the opposite side of the trade. A high number of speculators makes it cheaper and easier to hedge. But speculators are opportunists who try to corner the market and seek to make short-term profits by engaging in price and volume manipulations. One way of curtailing these short-term manipulative trading activities is by imposing higher taxes on short-term profits as compared to long-term capital gains.
 Legalised gambling – Though derivatives bring excessive benefits to the financial sector, the widespread speculation and the unchecked use of leverage enables FMPs to take unsustainable and unhedged positions in various contracts. Sudden shocks spread panic, trigger margin calls that lead to the untimely closing of positions or defaults, thereby making the markets extremely volatile, and enhancing the systematic risk. Instability spreads throughout the market and many players exit for good.
Legalised gambling – Though derivatives bring excessive benefits to the financial sector, the widespread speculation and the unchecked use of leverage enables FMPs to take unsustainable and unhedged positions in various contracts. Sudden shocks spread panic, trigger margin calls that lead to the untimely closing of positions or defaults, thereby making the markets extremely volatile, and enhancing the systematic risk. Instability spreads throughout the market and many players exit for good.
 However various regulatory requirements are now in place to keep a check and smooth the performance of OTC markets. CCPs (Central Counterparty Clearing) now play an important role and aim to reduce operational, settlement, legal, and default risk for traders. Collateral management is widely used in order to mitigate credit risk.
However various regulatory requirements are now in place to keep a check and smooth the performance of OTC markets. CCPs (Central Counterparty Clearing) now play an important role and aim to reduce operational, settlement, legal, and default risk for traders. Collateral management is widely used in order to mitigate credit risk.
Even though a Derivative contract may seem intricate or exotic, it is all about two parties coming together with an intent to trade or exchange a cash flow, a liability, or a risk depending on their level of tolerance.